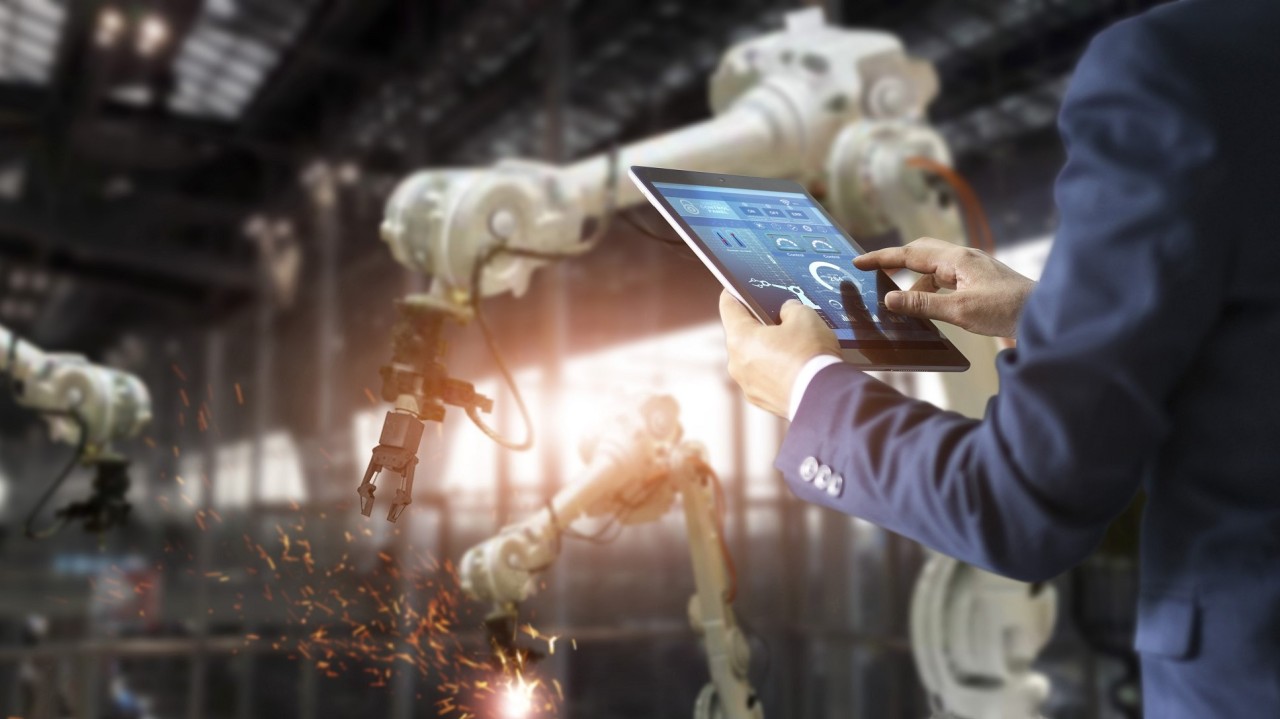
Industrial products form the backbone of manufacturing and infrastructure development, providing essential components, equipment, and machinery that power various industries worldwide. From heavy machinery and equipment to industrial chemicals and materials, these products play a crucial role in driving efficiency, productivity, and innovation across diverse sectors. This article explores the significance of industrial products, their key categories, and their impact on industrial development and economic growth.
Understanding Industrial Products
Industrial products encompass a wide range of goods used in industrial processes, manufacturing operations, and infrastructure development. These products serve as building blocks for various industries, providing essential inputs, tools, and machinery required for production, construction, and maintenance activities. Industrial products can be categorized based on their function, application, and end-user industries, ranging from machinery and equipment to raw materials and components.
Key Categories of Industrial Products
- Machinery and Equipment: Machinery and equipment are essential for manufacturing processes, construction projects, and industrial operations. This category includes a diverse range of products, such as machine tools, industrial robots, conveyors, pumps, compressors, and packaging machinery, that enable automation, precision, and efficiency in production processes.
- Industrial Chemicals and Materials: Industrial chemicals and materials are used in various industrial applications, from manufacturing and processing to construction and infrastructure development. This category encompasses chemicals, polymers, metals, alloys, ceramics, and composite materials that serve as raw materials, intermediates, or additives in industrial processes.
- Electrical and Electronic Components: Electrical and electronic components are integral to modern industrial systems, providing power, control, and connectivity solutions for machinery, equipment, and automation systems. This category includes components such as motors, sensors, actuators, switches, circuit boards, and cables used in industrial automation, electrical systems, and electronic devices.
- Safety and Protective Equipment: Safety and protective equipment are essential for ensuring the health, safety, and well-being of workers in industrial environments. This category includes personal protective equipment (PPE), safety gear, safety barriers, fire suppression systems, and emergency response equipment designed to mitigate risks and prevent accidents in industrial settings.
- Tools and Consumables: Tools and consumables are used for maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) activities in industrial facilities and manufacturing plants. This category includes hand tools, power tools, abrasives, lubricants, adhesives, and fasteners required for routine maintenance, equipment servicing, and production support tasks.
Impact of Industrial Products
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Industrial products enable businesses to improve operational efficiency, enhance productivity, and optimize resource utilization. Machinery, equipment, and automation systems streamline production processes, reduce manual labor, and increase output, leading to cost savings and competitive advantages for industrial enterprises.
- Innovation and Technological Advancement: Industrial products drive innovation and technological advancement across industries, fostering the development of cutting-edge technologies, materials, and solutions. Advanced machinery, automation systems, and digital technologies enable manufacturers to achieve higher levels of precision, quality, and customization in their products and processes.
- Infrastructure Development and Economic Growth: Industrial products play a vital role in infrastructure development, construction projects, and urbanization initiatives, driving economic growth and development. Construction machinery, building materials, and infrastructure components support the expansion of transportation networks, energy systems, and urban infrastructure, creating jobs and stimulating economic activity.
- Global Trade and Supply Chain Integration: Industrial products contribute to global trade and supply chain integration, facilitating the exchange of goods and services across borders. Raw materials, components, and finished goods are traded internationally, enabling manufacturers to access new markets, source cost-effective inputs, and diversify their supply chains to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
- Environmental Sustainability and Resource Efficiency: Industrial products play a crucial role in promoting environmental sustainability and resource efficiency through innovations in materials, processes, and technologies. Sustainable materials, energy-efficient equipment, and eco-friendly solutions help reduce environmental impact, minimize waste generation, and conserve natural resources, contributing to a greener and more sustainable industrial ecosystem.
Conclusion
Industrial products are indispensable components of modern industrial systems, providing the tools, equipment, and materials that drive efficiency, productivity, and innovation across industries. From machinery and equipment to chemicals and materials, industrial products enable businesses to meet the demands of a dynamic and competitive global market while promoting sustainability and economic growth. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and responsible stewardship, industrial product manufacturers can continue to drive industrial development and shape the future of manufacturing and infrastructure worldwide.…