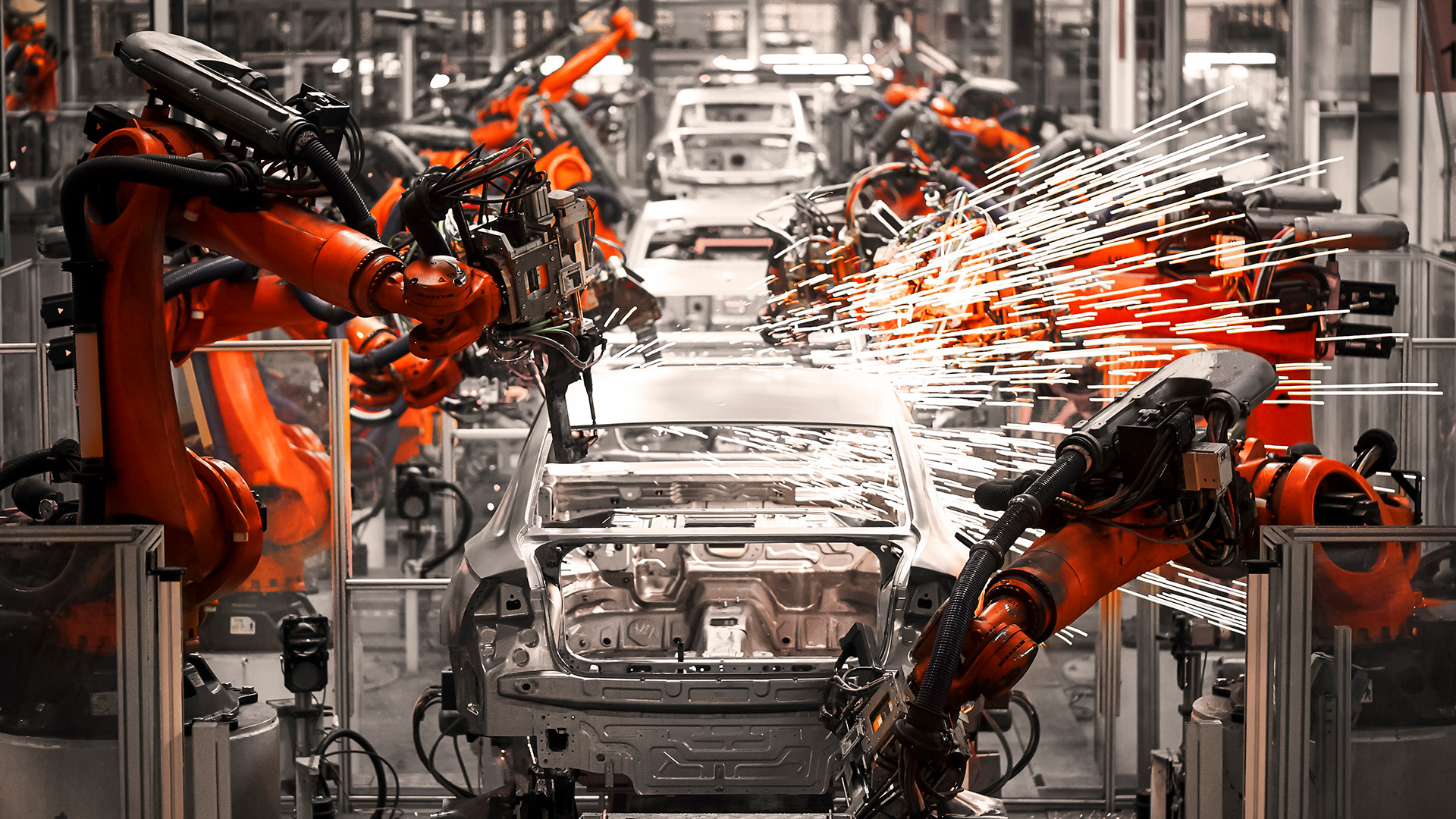
Resource manufacturing is a vital segment of the industrial landscape, encompassing the extraction, processing, and production of raw materials into usable goods. This sector forms the foundation of various industries, from construction and automotive to technology and pharmaceuticals. As global demand for resources increases, the practices and technologies associated with resource manufacturing are evolving to meet both economic needs and environmental challenges. This article explores the importance of resource manufacturing, its processes, challenges, and future trends.
Understanding Resource Manufacturing
Resource manufacturing refers to the entire process of obtaining raw materials from the Earth and transforming them into finished products. This includes industries involved in mining, forestry, agriculture, and fishing, as well as the subsequent processing of these materials. The resources produced are crucial for countless applications, from building infrastructure to creating consumer goods.
Key Components of Resource Manufacturing
- Extraction: This is the first step in resource manufacturing, where raw materials are harvested from the Earth. This can involve mining metals and minerals, logging timber, or harvesting crops and fish.
- Processing: Once extracted, raw materials must be processed to make them suitable for manufacturing. This can include refining metals, milling grains, or treating wood. Processing often involves various chemical, physical, and mechanical methods to convert raw materials into a form that can be used in production.
- Manufacturing: After processing, the materials are transformed into finished goods. This can involve assembly, packaging, and quality control to ensure that the final products meet industry standards.
Importance of Resource Manufacturing
Resource manufacturing is fundamental to the economy for several reasons:
- Economic Contribution: It generates significant revenue and employment. Many countries depend on resource extraction and processing as key economic drivers, particularly those rich in natural resources.
- Supply Chain Foundation: Resource manufacturing provides essential materials for other industries. Construction relies on metals, plastics, and timber; the automotive industry requires various metals and plastics; and technology relies on rare earth elements and components manufactured from these resources.
- Innovation and Development: As technology advances, resource manufacturing is becoming more efficient and sustainable. Innovations in extraction and processing techniques are leading to reduced waste and energy consumption.
Challenges in Resource Manufacturing
Despite its importance, the resource manufacturing sector faces numerous challenges:
1. Environmental Concerns
Resource extraction often leads to environmental degradation, including deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution. The challenge is to balance economic needs with environmental sustainability. Many industries are now adopting practices to minimize their ecological footprints, such as using renewable energy sources and implementing waste recycling programs.
2. Regulatory Pressures
Governments worldwide are increasingly implementing regulations to ensure sustainable practices in resource manufacturing. Compliance with environmental laws and standards can be costly and complex for manufacturers, requiring significant investment in new technologies and processes.
3. Market Volatility
The prices of raw materials can fluctuate significantly due to factors such as geopolitical tensions, economic downturns, and changes in demand. This volatility can affect profitability and planning for resource manufacturers, making it crucial to adopt flexible business strategies.
4. Labor Shortages
As the manufacturing landscape evolves, there is a growing demand for skilled labor in resource manufacturing. However, many regions face shortages of workers with the necessary technical skills, leading to challenges in maintaining productivity and innovation.
Future Trends in Resource Manufacturing
The future of resource manufacturing is likely to be shaped by several key trends:
1. Sustainable Practices
The push for sustainability is transforming resource manufacturing. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as reducing waste, minimizing energy consumption, and using sustainable materials. Circular economy principles, which focus on reusing and recycling materials, are becoming more prevalent in the industry.
2. Technological Advancements
Technological innovation is driving efficiency and productivity in resource manufacturing. Automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence are being integrated into processes, allowing for greater precision and reduced labor costs. Additionally, advancements in data analytics enable manufacturers to optimize operations and predict market trends more accurately.
3. Digitalization and Industry 4.0
The integration of digital technologies, commonly referred to as Industry 4.0, is transforming resource manufacturing. The use of IoT devices, big data analytics, and cloud computing enables real-time monitoring and management of production processes. This digital transformation enhances operational efficiency and responsiveness to market changes.
4. Resilient Supply Chains
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains. As a result, many manufacturers are reevaluating their supply chain strategies to enhance resilience. This includes diversifying suppliers, increasing local sourcing, and investing in technology to improve supply chain visibility and flexibility.
5. Focus on Renewable Resources
The demand for renewable resources is rising, driven by consumer preferences for sustainable products. Resource manufacturers are exploring alternatives to traditional materials, such as biodegradable plastics, sustainable forestry practices, and organic agricultural methods.
Conclusion
Resource manufacturing is a critical component of the global economy, providing essential materials for various industries while driving innovation and