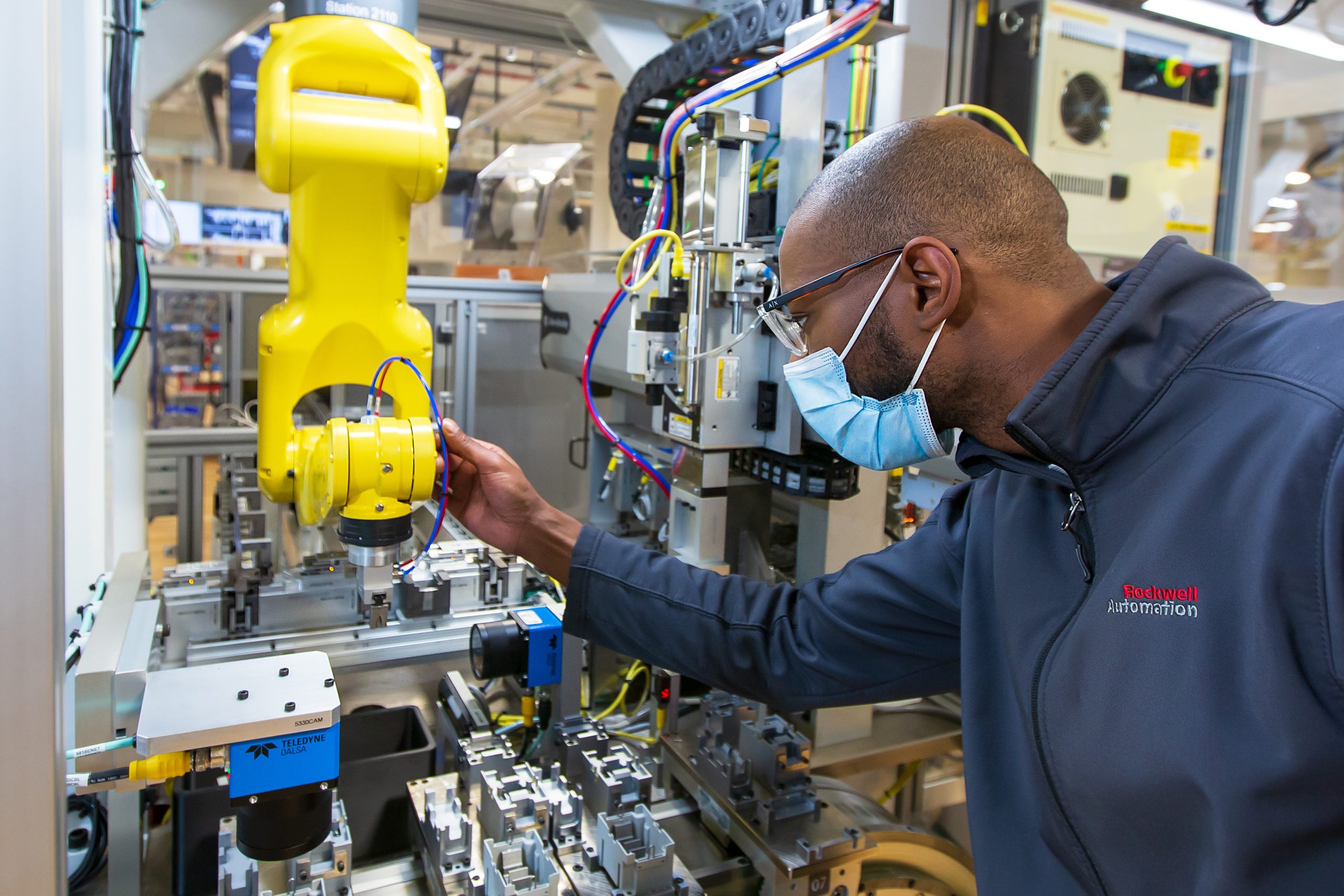
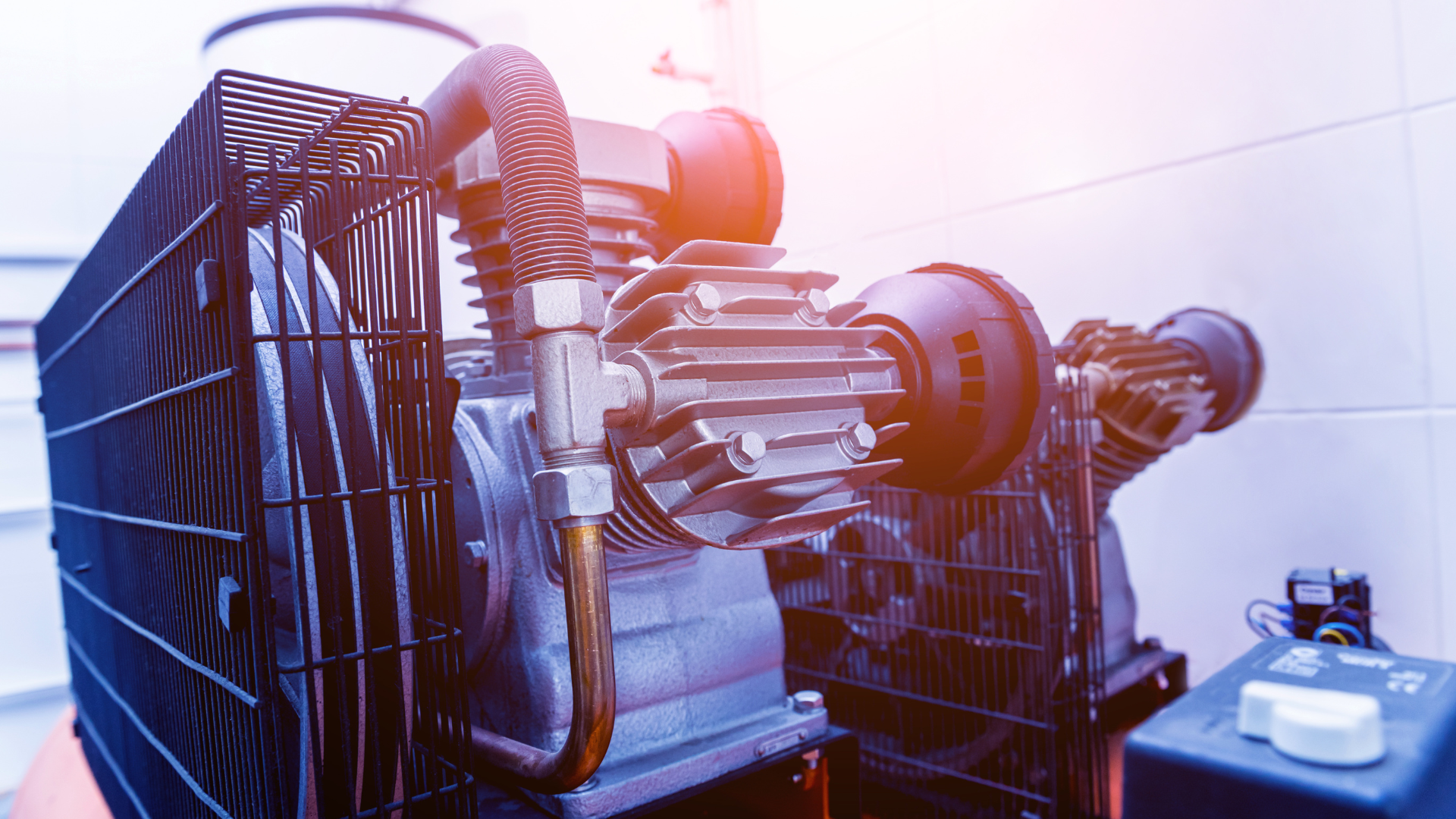
Industrial products form the backbone of modern manufacturing and infrastructure, powering economies, driving innovation, and shaping everyday life. From machinery and equipment to raw materials and components, industrial products encompass a vast array of goods used in various industries and sectors worldwide. In this article, we delve into the realm of industrial products, exploring their significance, characteristics, and applications across diverse domains.
Understanding Industrial Products
Industrial products refer to goods and materials used in manufacturing, construction, and other industrial processes to produce finished goods or provide services. These products serve as essential inputs, tools, and assets in the production, distribution, and maintenance of goods and services across a wide range of industries. Industrial products can be categorized based on their nature, purpose, and application, including machinery, equipment, raw materials, parts, components, and consumables.
Characteristics and Attributes
Industrial products exhibit several key characteristics and attributes that distinguish them from consumer goods and products:
- Durability and Reliability: Industrial products are designed and engineered for durability, reliability, and longevity to withstand harsh operating conditions and heavy usage in industrial environments. They undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure consistent performance and reliability over time.
- Specialization and Customization: Industrial products often feature specialized designs, specifications, and configurations tailored to specific industry requirements and applications. Manufacturers offer customization options to meet unique customer needs, preferences, and performance criteria.
- Technical Complexity: Industrial products may involve intricate designs, advanced technologies, and complex manufacturing processes due to their specialized functions and performance requirements. They incorporate sophisticated components, materials, and engineering principles to achieve optimal performance and efficiency.
- Scalability and Compatibility: Industrial products are designed to be scalable and compatible with existing systems, machinery, and equipment in industrial settings. They integrate seamlessly into production processes, supply chains, and operational workflows to enhance productivity and efficiency.
- Safety and Compliance: Industrial products adhere to stringent safety standards, regulatory requirements, and industry certifications to ensure user safety, product compliance, and regulatory compliance. Manufacturers prioritize safety features, risk mitigation measures, and compliance documentation to protect workers, facilities, and the environment.
Applications and Industries
Industrial products find applications across a diverse range of industries and sectors, contributing to manufacturing, infrastructure development, and economic growth worldwide:
- Manufacturing and Production: Industrial products play a vital role in manufacturing and production processes, providing machinery, equipment, tools, and materials for fabrication, assembly, and packaging operations. They enable mass production, precision manufacturing, and quality control in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods.
- Construction and Infrastructure: Industrial products are essential for construction projects, infrastructure development, and building maintenance activities. They include building materials, construction machinery, structural components, and safety equipment used in residential, commercial, and civil engineering projects.
- Energy and Utilities: Industrial products support energy generation, transmission, and distribution activities in the energy and utilities sector. They encompass power generation equipment, renewable energy systems, transmission lines, substations, and utility meters used in electricity, gas, and water networks.
- Transportation and Logistics: Industrial products facilitate transportation, logistics, and supply chain management operations across global markets. They include vehicles, aircraft, ships, railways, containers, packaging materials, and logistics systems used in freight transportation, warehousing, and distribution networks.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: Industrial products are integral to healthcare delivery, medical diagnostics, and pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. They encompass medical devices, laboratory equipment, diagnostic instruments, pharmaceutical ingredients, and packaging materials used in hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and pharmaceutical facilities.
Market Trends and Innovations
The industrial products market is subject to various trends, innovations, and advancements shaping the industry landscape:
- Industry 4.0 and Digital Transformation: The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as automation, robotics, Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI), is transforming industrial product manufacturing and operations. Smart factories, digital twins, and predictive maintenance solutions optimize production efficiency, quality control, and supply chain management.
- Sustainability and Green Technologies: Increasing emphasis on sustainability, environmental conservation, and resource efficiency is driving demand for eco-friendly industrial products and green technologies. Manufacturers are developing energy-efficient equipment, recyclable materials, and renewable energy solutions to minimize environmental impact and support sustainable development goals.
- Supply Chain Resilience and Localization: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of supply chain resilience, risk mitigation, and localization strategies in the industrial products sector. Manufacturers are diversifying supply chains, reshoring production, and adopting agile manufacturing practices to enhance supply chain flexibility and responsiveness to market disruptions.
- Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing, including 3D printing, is revolutionizing industrial product design, prototyping, and production processes. These technologies enable rapid prototyping, on-demand manufacturing, and customization of complex parts and components, reducing lead times and production costs.
- Circular Economy and Product Lifecycle Management: The transition towards a circular economy model is driving initiatives for product lifecycle management, waste reduction, and resource recovery in the industrial products sector. Manufacturers are implementing