Product manufacturing is a crucial sector that transforms ideas and raw materials into tangible goods. It encompasses a wide range of industries and processes, from consumer electronics and automobiles to pharmaceuticals and clothing. This article provides an overview of the key aspects of product manufacturing, explores current trends, and looks ahead to future developments shaping the industry.
Core Processes in Product Manufacturing
- Design and Development: The manufacturing process begins with product design and development. This phase involves conceptualizing the product, creating prototypes, and refining designs based on feedback. Design teams use tools such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to create detailed models and specifications that guide the production process.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right materials is critical for ensuring product quality and performance. Manufacturers must consider factors such as strength, durability, cost, and environmental impact when selecting materials. Common materials include metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Advanced materials like nanomaterials and smart materials are also increasingly used for their enhanced properties.
- Production Planning: Production planning involves developing a strategy for manufacturing the product, including determining the necessary equipment, workforce, and production methods. It includes scheduling, resource allocation, and quality control measures to ensure the manufacturing process runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Manufacturing Methods: The choice of manufacturing methods depends on the product type, complexity, and volume. Common methods include:
- Casting: Pouring molten material into molds to create complex shapes.
- Machining: Removing material from a solid block using tools such as lathes and mills.
- Injection Molding: Injecting molten material into molds to produce precise and complex parts.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Building up layers of material to create parts and prototypes.
- Assembly: Combining various components into a finished product, often involving manual or automated processes.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that products meet specified standards is essential for customer satisfaction and regulatory compliance. Quality control involves inspecting and testing products at various stages of production to identify and address defects. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) and Six Sigma are used to monitor and improve quality.
Current Trends in Product Manufacturing
- Industry 4.0: The fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0, represents a shift towards smarter and more interconnected manufacturing. It involves integrating digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics into production processes. These technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved operational efficiency.
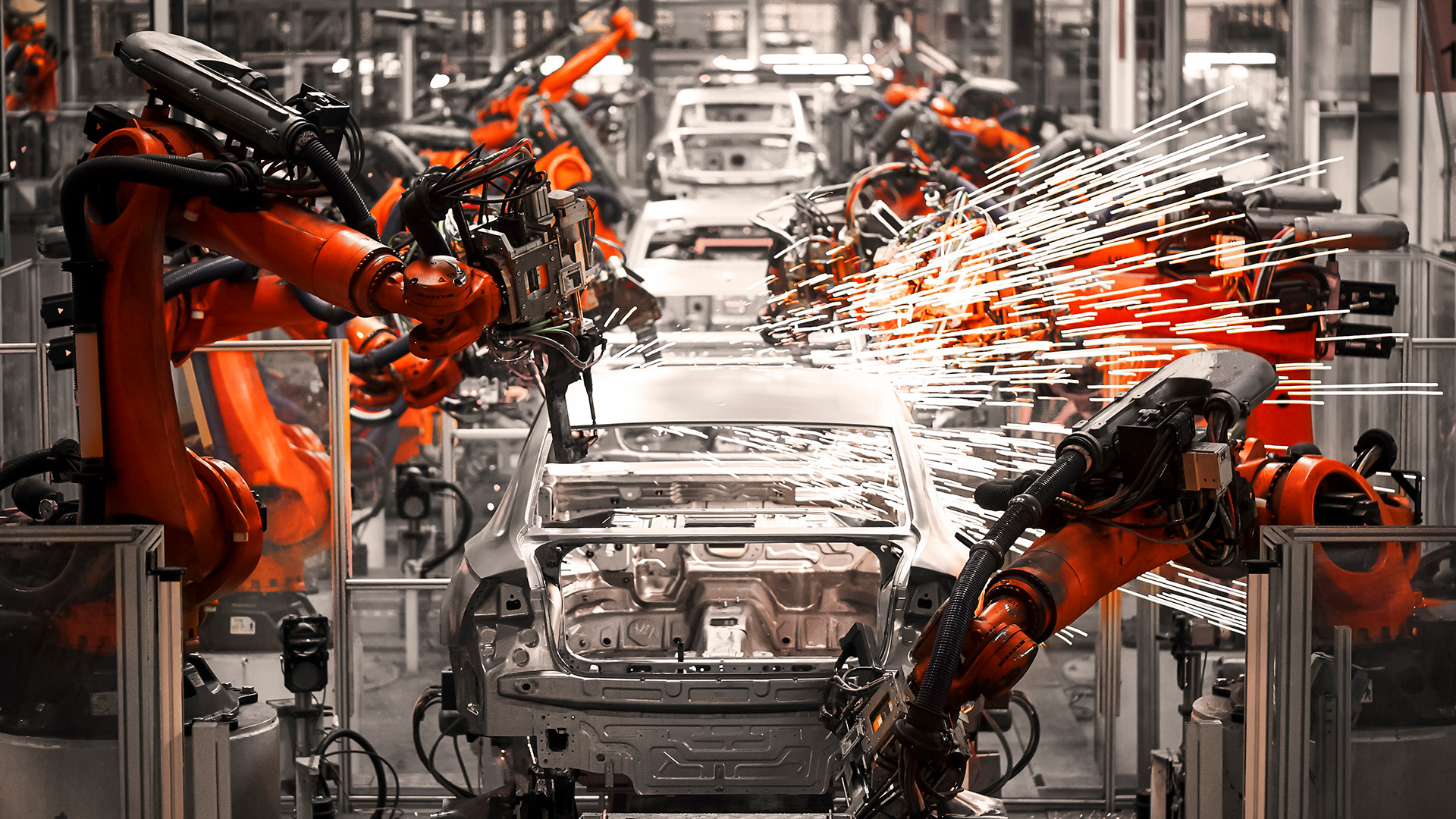
- Automation and Robotics: Automation and robotics are transforming manufacturing by enhancing productivity, precision, and flexibility. Advanced robots equipped with AI and machine learning capabilities can perform complex tasks, work alongside human operators, and adapt to changing production requirements. Automation reduces labor costs and minimizes human error, leading to more consistent product quality.
- Sustainability: Sustainability is a growing concern in product manufacturing. Companies are adopting green practices to reduce their environmental impact, such as using energy-efficient processes, minimizing waste, and utilizing recyclable materials. Sustainable manufacturing practices help address environmental challenges and meet consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
- Customization and Personalization: The demand for customized and personalized products is increasing. Advances in manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing and flexible production systems, allow for on-demand and batch-size-one production. This trend enables manufacturers to offer tailored products that meet individual customer preferences and needs.
- Smart Manufacturing: Smart manufacturing leverages data-driven insights and advanced technologies to create highly efficient and adaptive production systems. By using IoT sensors, AI, and machine learning, manufacturers can optimize processes, improve product quality, and enhance overall operational performance.
Future Directions in Product Manufacturing
- Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets or processes. They simulate real-world conditions and enable manufacturers to test and optimize operations in a digital environment before making changes to the physical system. Digital twins help improve decision-making, reduce downtime, and enhance product development.
- Advanced Materials: The development of advanced materials, such as nanomaterials and smart materials, is expected to drive innovation in product manufacturing. These materials offer enhanced properties, such as increased strength, reduced weight, and improved functionality, leading to new applications and product designs.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning will continue to play a significant role in manufacturing. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to optimize production schedules, improve quality control, and predict maintenance needs. AI-driven insights will enhance decision-making and drive innovation in manufacturing processes.
- Circular Economy: The concept of a circular economy focuses on creating a closed-loop system where resources are continuously reused, recycled, and regenerated. Manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate circular economy principles into their processes, such as designing products for disassembly, using recycled materials, and implementing take-back programs.
- Globalization and Localization: The balance between globalization and localization in manufacturing is evolving. While global supply chains offer cost advantages, there is a